2 Headphones for Hearing Impaired Meaning: Hear Every Word While Watching TV It aims to enlighten you and make you more inclusive and understanding.
Hearing impairment, or hearing loss, includes many conditions that affect how we hear. It can range from mild to severe, even causing deafness. These issues can affect one or both ears and may last a short time or forever, depending on the cause.
Discover a breakthrough solution that can help manage tinnitus, providing clearer hearing and improved brain function.
Key Takeaways
- Hearing impairment refers to a partial or total inability to hear sounds, ranging from mild to profound deafness.
- Hearing loss can affect one or both ears and may be temporary or permanent, depending on the cause.
- Understanding the meaning of “hearing impaired” is crucial for providing appropriate support and resources for those affected.
- Assistive technologies, such as hearing aids and cochlear implants, can enhance the auditory experience for individuals with hearing impairments.
- Communication methods, including sign language interpretation and lip reading, can help bridge the gap for those with hearing disabilities.
Understanding Hearing Impairments: An Overview
Hearing impairment comes in many forms, each with its own set of characteristics and causes. Understanding these complexities is key to keeping your hearing healthy and improving communication.
Defining Hearing Loss and Deafness
Hearing loss covers a wide range, from mild to severe. Conductive hearing loss happens when sound waves can’t pass through the outer ear, eardrum, or middle ear. Sensorineural hearing loss is the most common, caused by damage to the inner ear or nerve pathways. Mixed hearing loss combines both conductive and sensorineural types. Deafness is the most severe form, making communication and accessibility very challenging.
Take control of your hearing with this innovative solution that can help alleviate tinnitus and improve auditory function.
Types of Hearing Impairments
There are several types of hearing impairments, each with its own causes and effects:
- Conductive Hearing Loss: Caused by issues like too much earwax, infections, or damaged eardrum.
- Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Damaged hair cells in the cochlea, often from loud noises.
- Mixed Hearing Loss: A mix of conductive and sensorineural, often from infections.
- Prelingual Deafness: Unable to hear before learning to speak.
- Post-lingual Deafness: Loses hearing after learning to speak, often from medication or infections.
- Single-sided Deafness (SDD): Difficulty in conversation and sound localization due to hearing loss in one ear.
“Around 15% of people in the United States over the age of 18 report some level of hearing loss.”
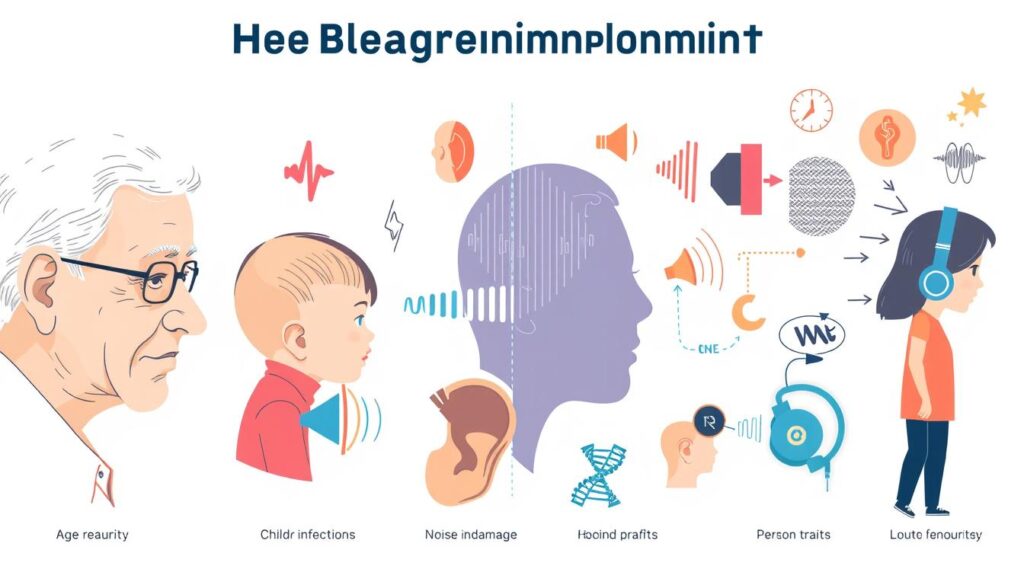
Causes of Hearing Impairments Across the Lifespan
Hearing impairments come from many sources, like genes and the environment. Knowing why hearing loss happens at different ages helps us prevent and manage it better.
Prenatal and Perinatal Causes
Genetic factors, intrauterine infections, and birth asphyxia often cause hearing loss before birth. These issues can harm a baby’s hearing system, affecting their hearing development.
Childhood and Adolescent Causes
In kids and teens, ear infections, meningitis, and other diseases can lead to hearing loss. Also, some genetic conditions and birth defects can show up during these years.
Adult and Older Age Causes
As people get older, chronic diseases and age-related hearing loss become more common. Noise exposure and conditions like otosclerosis and tinnitus can also affect adults.
Throughout life, things like earwax buildup, trauma, and certain medicines can cause hearing loss. Early action and prevention can help reduce the effects of hearing loss and keep our hearing sharp.
Try this tinnitus solution to not only regain 20/20 hearing but also enjoy better cognitive function.“Hearing loss is a common problem that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Understanding the diverse causes of hearing impairments is essential for developing comprehensive strategies to address this critical health concern.”
The Impact of Unaddressed Hearing Impaired Meaning
Unaddressed hearing loss can deeply affect many areas of life. This includes communication, social interactions, education, and work. It can cause big problems for people, communities, and the world’s economy.
One big issue is how it affects talking and learning. Kids with untreated hearing loss might have trouble learning language and thinking clearly. Adults with unaddressed hearing loss often struggle to talk well, leading to feeling alone and being judged.
Ignoring hearing loss can also hurt education and jobs. Research shows people with hearing loss face big challenges in school and work. Deaf students are more likely to drop out of high school. They also have fewer job chances, leading to more people needing social security.
The cost of not treating hearing loss is huge, about $980 billion a year. Most of this cost falls on poor and middle-income countries. These places often can’t get the hearing care they need. This shows we really need to spend more on hearing health to solve this big problem.
“Hearing loss has a significant impact on society and economy, affecting aspects such as communication, cognition, social isolation, education, and employment.”
We need to tackle hearing loss in many ways. Finding hearing problems early and treating them can make a big difference. Things like checking newborns’ hearing, protecting workers’ ears, and teaching safe listening can help a lot.
By understanding and tackling hearing loss, we can help people, build stronger communities, and make the world a fairer place.
Prevention Strategies for Hearing Loss
Many causes of hearing loss can be prevented. Public health measures and clinical interventions help across our lives. By being proactive, you can protect your hearing and avoid permanent damage.
Public Health Measures
Prevention starts in the community. Immunizations protect against infections that can harm hearing. Good maternal and childcare practices, along with genetic counseling, help catch ear problems early.
Raising awareness about hearing health is key. It helps fight the dangers of loud noises.
Occupational and Recreational Strategies
Workplaces can reduce hearing loss with good programs. These include monitoring noise, using engineering controls, and providing hearing protection. Regular hearing tests are also important.
Discover how you can enhance your hearing and prevent further damage by addressing tinnitus with this highly effective product.
In free time, promote safe listening. Turn down the volume on personal devices and wear ear protection at loud events. This helps keep your hearing safe.
Understanding the complexities of hearing impairment is essential for improving communication, inclusivity, and support for those affected. Prevention, early intervention, and the use of assistive technologies like hearing aids and implants can greatly enhance the lives of people with hearing loss.
If you or someone you know struggles with tinnitus or hearing loss, there is a solution. Take the step today to experience clearer hearing, better brain function, and a life free from the bothersome sounds of tinnitus.
Check out This Post: https://healthsuccesful.com/choosing-the-right-ear-protection-for-concerts-and-events/
FAQ
What is the meaning of hearing impaired?
Hearing impairment, or hearing loss, means you can’t hear sounds well. It can be mild or severe. Mild loss makes it hard to hear soft sounds or certain frequencies. Severe loss, or deafness, means you can barely hear anything.
What are the different types of hearing impairments?
There are three main types of hearing loss:
– Conductive hearing loss happens when sound can’t get through the ear properly.
– Sensorineural hearing loss is the most common. It’s caused by damage to the inner ear or the nerve paths to the brain.
– Mixed hearing loss is a mix of conductive and sensorineural loss.
What are the causes of hearing impairments across the lifespan?
Hearing loss can be caused by different things at different ages:
– Before birth and at birth, it can be due to genetics, infections, or lack of oxygen.
– In kids and teens, it might be from infections, meningitis, or other diseases.
– Adults and seniors might lose hearing from chronic diseases, smoking, or age-related problems.
How can unaddressed hearing impairment impact an individual’s life?
Not treating hearing loss can really affect your life. It can make talking and understanding others hard. This can lead to feeling left out, struggling in school or work, and feeling stigmatized.
What are some prevention strategies for hearing loss?
To prevent hearing loss, there are several steps you can take:
– Get vaccinated to avoid infections.
– Practice good ear care, like cleaning and avoiding loud noises.
– Use safe listening practices, like wearing ear protection.
– Manage ear infections and use medicines wisely to avoid damage.
– These actions can help a lot in preventing hearing loss worldwide.
Source Links
- Hearing Impairments – https://ung.edu/student-accessibility-services/resources-and-links/faculty-information/hearing-impairments.php
- Hearing Impaired People: a Multitude of Profiles for Different Needs – https://www.inclusivecitymaker.com/hearing-impaired-people-multitude-profiles-different-needs/
- What is a Hearing Impairment? Special Education Guide – https://www.specialeducationguide.com/disability-profiles/hearing-impairments/
- Deafness and hearing loss: Causes, symptoms, and treatments – https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/249285
- Hearing loss – Symptoms and causes – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hearing-loss/symptoms-causes/syc-20373072
- Age-Related Hearing Loss (Presbycusis) — Causes and Treatment – https://www.nidcd.nih.gov/health/age-related-hearing-loss
- Hearing loss – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hearing_loss
- Age-Related Hearing Loss (Presbycusis) – https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/presbycusis
- Deafness and hearing loss – https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/deafness-and-hearing-loss
- Impact of Hearing Loss on Daily Life and the Workplace – Hearing Loss – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK207836/
- Hearing loss – https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/hearing-loss
- How Can I Prevent Hearing Loss? (for Teens) – https://kidshealth.org/en/teens/hearing-impairment.html